Generated Backend Code
Overview
WaveMaker generates fully readable, standards-based Java backend code.
The code is not black-boxed and follows established enterprise patterns using Java, Spring, and Hibernate/JPA.
Developers have full access to the source code and can safely extend it without impacting platform upgrades.
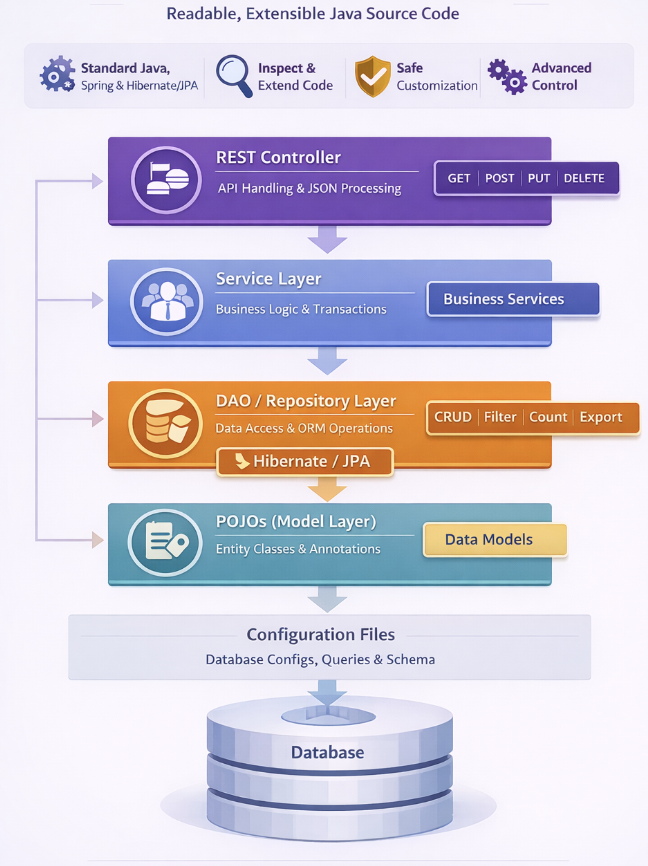
Backend Architecture
WaveMaker generates a standard layered backend architecture.
- REST Controllers handle HTTP requests
- Service layer contains business logic
- DAO / Repository layer manages persistence using Hibernate/JPA
- Entity models represent database tables
- Design-time metadata supports Studio features only
This architecture aligns with common Spring Boot application practices.
Project Structure
Generated backend code is organized under the services directory using a conventional Java package layout.
Each layer has a clear responsibility, making the codebase easy to understand, debug, and customize.
services/
└── mydatabase/
├── designtime/ # Files used during design-time
└── src/
└── com/
└── myApp/
├── controller/
├── service/
├── dao/
├── models/
└── *.java
Layers
Controller Layer (controller)
- Exposes REST APIs to clients
- Handles request and response processing, input validation and authorization, and JSON serialization/deserialization
- Implemented using Spring REST controllers and supports adding custom endpoints and security logic
Service Layer (service)
- Contains application and business logic
- Responsible for business rule implementation, transaction management, and coordinating between controllers and repositories
- Changes here are not overwritten during regeneration or upgrades
DAO / Repository Layer (dao)
- Handles database access using ORM (Hibernate/JPA)
- Implements CRUD operations, query execution, and result mapping
- Provides pagination, filtering, count and export operations; supports custom SQL queries and stored procedures
- Uses standard JPA repositories and does not rely on a proprietary data-access framework
Model Layer (models / Entities)
- Maps database schema to Java objects, defining fields and relationships
- Includes JPA annotations for table mapping
- Generated models are plain Java POJOs that are fully extensible and reusable
Design-time Configuration (designtime)
- Stores metadata used by WaveMaker Studio
- Used at design time; runtime uses generated Java code
Structure
services/
└── myDatabase/ # Main database service
└── designtime/ # Design-time metadata and configuration
├── db-connection-settings.json
├── db-rest-patch.json
├── myDatabase_API.json
├── myDatabase_procedure.json
├── myDatabase_published_dataModel.json
├── myDatabase_query.json
└── service-info.json
Application Configuration Properties
Whenever services are imported into WaveMaker, the platform automatically generates configuration properties that can be mapped to different environments such as Development, QA, or Production.
You can view and manage these properties in the Profiles.
For more information, refer to the Profiles section in the documentation.
For more details on environment-specific configurations, refer to the Deployment Profiles section.
Click to expand configuration properties
# Database Configuration (hrdb)
db.hrdb.dataSourceType=WM_MANAGED_DATASOURCE
db.hrdb.driverClass=org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver
db.hrdb.url=jdbc:hsqldb:file:{WebAppRoot}/WEB-INF/data/hrdb;shutdown=true;ifexists=true;hsqldb.lock_file=false;
db.hrdb.username=sa
db.hrdb.password=********
db.hrdb.schemaName=PUBLIC
db.hrdb.hbm2ddl=none
db.hrdb.minPoolSize=2
db.hrdb.maxPoolSize=4
db.hrdb.maxPageSize=100
db.hrdb.transactionTimeout=30
db.hrdb.jndiName=
Summary
WaveMaker generates a clean, layered, and extensible Java backend aligned with standard Spring practices.
Developers can inspect, extend, and maintain the codebase while benefiting from rapid API generation and upgrade-safe customization.
How-To Guides
Learn more about working with databases and queries through these practical guides:
- Connecting to Azure SQL Server - Configure Azure SQL Server database connections
- Uploading JDBC Drivers - Add custom JDBC drivers for database connectivity
- Configuring AWS Redshift Database - Set up Amazon Redshift connections
- Configuring SAP HANA Cloud Database - Integrate with SAP HANA Cloud
- MySQL Connection Using SSL - Secure MySQL connections with SSL/TLS
- Switch from MariaDB to MySQL Connector - Migration guide for connector changes
- Audit History Using CRUD Listeners - Track data changes and maintain audit trails