Generated Code
Overview
WaveMaker is not a black box. The platform generates fully readable, standards-based Java source code that follows proven enterprise architecture patterns. All backend artifacts are built using Java, Spring, and Hibernate/JPA, providing complete transparency and control to developers.
This approach enables teams to achieve low-code development speed while retaining the flexibility, extensibility, and governance expected from traditional enterprise applications.
Key Characteristics
- Backend services are generated using standard Java frameworks
- Source code is fully accessible and inspectable
- Custom business logic can be added without impacting platform upgrades
- Generated code follows layered architectural best practices
- Suitable for advanced enterprise and integration-driven use cases
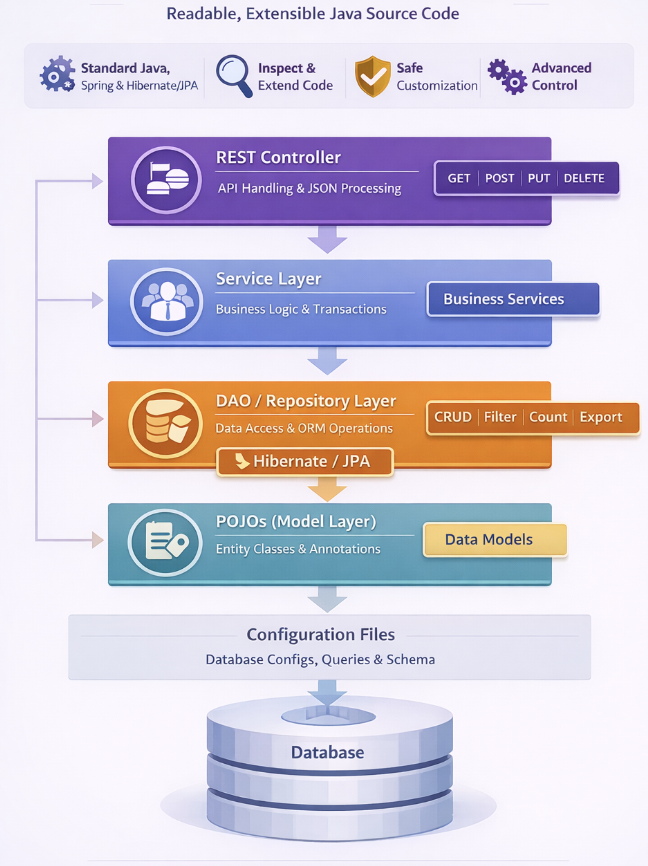
WaveMaker Generated Backend Architecture
This diagram illustrates the layered backend architecture generated by WaveMaker. Client requests are handled by REST controllers, processed through service-layer business logic, and persisted using DAO/repository components backed by Hibernate/JPA. Entity models represent database tables, while design-time configuration supports application development without impacting runtime execution. The architecture follows standard Java and Spring practices, ensuring transparency, extensibility, and enterprise readiness.
Generated Project Structure
WaveMaker generates a conventional Java project structure under the services directory, aligned with industry-standard backend design principles.
Each layer has a clearly defined responsibility, ensuring separation of concerns, maintainability, and extensibility.

Layered Architecture
REST Controller Layer (controller)
Purpose
Acts as the API entry point for client applications.
Responsibilities
- Expose RESTful endpoints
- Handle request and response lifecycle
- Perform authorization and request validation
- Marshal and unmarshal JSON payloads
Implementation Notes
- Implemented using standard Spring REST controllers
- Can be extended to add custom endpoints or security logic
Service Layer (service)
Purpose
Encapsulates business logic and application workflows.
Responsibilities
- Implement business rules
- Validate input data
- Manage transactions
- Coordinate interactions between controllers and DAO layer
Implementation Notes
- Recommended layer for adding custom logic
- Isolated from regeneration during platform upgrades
DAO / Repository Layer (dao)
Purpose
Provides database access using ORM abstractions.
Responsibilities
- Interact with the database via Hibernate/JPA
- Execute persistence operations
- Abstract database-specific logic
Generated Capabilities
- CRUD APIs for each entity
- Filter APIs
- Count APIs
- Export APIs
- Support for custom queries and stored procedures
Implementation Notes
- Uses standard JPA repositories
- Avoids proprietary data-access abstractions
Model Layer (models and Entity Classes)
Purpose
Represents database tables as Java objects.
Responsibilities
- Define entity fields and relationships
- Map database schema using JPA annotations
- Serve as data carriers across application layers
Implementation Notes
- Plain Old Java Objects (POJOs)
- Fully extensible and reusable
Design-time Configuration (designtime)
Purpose
Stores metadata required by WaveMaker Studio during application design.
Contents
- Database connection definitions
- API specifications
- Query and procedure metadata
- Schema information
Implementation Notes
- Used exclusively at design time
- Runtime execution depends only on generated Java source code
ORM Artifacts
WaveMaker generates ORM artifacts that conform to Hibernate/JPA standards:
- Entity classes
- Repository interfaces
- Generated CRUD methods
- Query definitions and mappings
Summary
WaveMaker combines the productivity of low-code development with the robustness of high-code architectures by generating transparent, layered, and standards-based backend services. Developers retain full ownership and control of the code while benefiting from rapid application delivery.